The only conditions – either you have formatted your drive or connected a new HDD or SSD as the replacement/upgradation of the existing one, you will be needed to make a choice between MBR or GPT.
If this is the very first time, you are coming across to these technical abbreviations, let me tell you MBR and GPT stands for Master Boot Record and GUID Partition Table, respectively. These are the standard for the layout of the partition table on a physical hard disk that defines how data is stored on it. And if you think that making a random choice between MBR and GPT doesn’t make any difference and have no significant effect over important aspects than you are sadly mistaken.
So if you want to know which one to choose MBR or GPT and is alongside compatible working with your system, you have got the information at your fingertips. This comprehensive guide is an endeavor towards simplifying the difference between MBR and GPT disk partition, how to choose the best, and the method to convert.
I can assert, after fishing reading this article, you wouldn’t want to lurk around any further.
MBR vs GPT – The Disk Partition Style
Before a hard disk can be used it needs to have a partition scheme configured on it. The partition scheme allows the hard disk to be divided up into partitions.
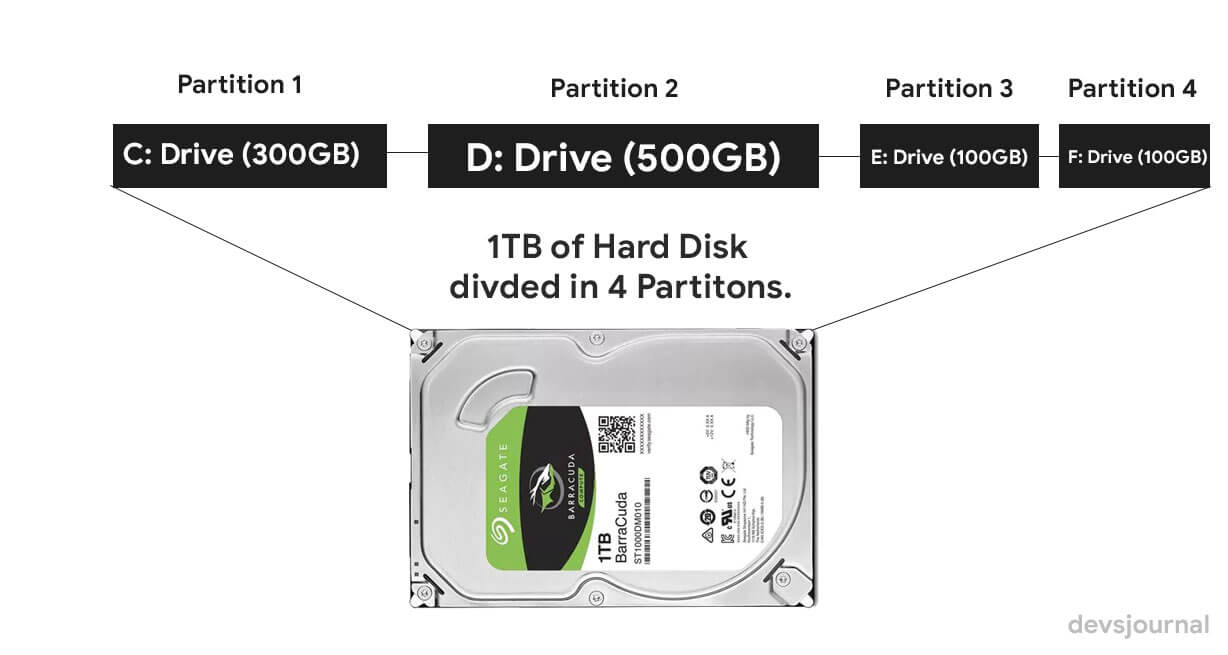
Let’s take a typical hard disk as shown above. The hard disk contains space that can be used for data. Before this space can be used, it needs to be divided up into partitions. Once a partition is created, it can be formatted by the operating system and data stored on it. There are two different partition tables that are available. These are, MBR and GPT. MBR is the older of the two and thus has the most compatibility with operating systems and hardware. GPT is the newer standard and has more features but requires certain hardware in order to work.
MBR and GPT are the two methods used for defining how the information is structured on the partitions, where partitions begin and end, and more. Partitions, in particular, are the sections on the drive that store data. It is mandatory to have at least need one partition on the drive because without it you won’t be able to save or store anything onto the disk.
However, in a nutshell, GPT is a UEFI associated newer standard that comes with many advantages and is the most suitable one for the modern systems. Also, MBR is none to the second for its compatibility and is the old and most commonly used disk layout.
When setting up a new disk partition on Windows, you will always find MBR as default that makes it more likely to be the choosable one for most of us. But it doesn’t matter much if initially, you have chosen MBR for the initialization of the disk partition since you can always change it to GPT later on.
Also Read: Where do deleted files go? Do they occupy space after deletion?
Difference between MBR & GPT
Following are the most significant and notable factors that show differences between MBR and GPT partitioning styles.
1. Disk Partition Limitation
The number of partitions you can create on a hard disk solely depends on the device’s partition style.
For MBR, you are only allowed to create up to 4 primary partitions. However, if you want to have more, by modifying one of the primary partition as an “Extended partition,” you can create an unlimited number of logical drives or partitions inside it. This is just a small hack that you can employ to circumvent the limitation of Master Boot Record. But keep in mind, logical partitions can’t hold Windows operating system files since they aren’t the Boot partitions (primary.)
GPT is another partitioning scheme, which overcomes the disk partition limitation of MBR. The size limits of the GPT based drives depend on the operating system and its file systems. For Windows OS, users can create up to 128 partitions on a GPT drive with no need of an extended partition whatsoever.
2. Capacity
MBR can only use the storage space up to 2TB, that means anything larger, the rest disk space would be indicated as unallocated and unusable. Isn’t it a complete waste of your disk capacity? You can see that all though MBR can offer the basic features a user requires, its days are numbered due to the limitation of how much hard disk space it can access.
The replacement for MBR is GPT or GUID Partition table. GPT supports 128 partitions without the need to change an existing partition into an extended partition like MBR requires. GPT supports hard disks sizes in Zettabytes. The actual amount varies depending on what size the hard disk manufacturer makes the sectors on the hard disk, but either way a Zettabyte is a lot of data. Currently with Terabyte hard disks on the market, first a Petabyte and Exabyte hard disks need to be made before we get close to a Zettabyte hard disk.
And for GPT, there is no such disk capacity limitation. Technically, it provides 64 bits for logical block addresses that allow GUID Partition Table to support up to 9.4 Zettabyte for the disk capacity. In simple words, the GPT partitioning style has no real-world limitation and allow you to utilize the full storage of the disk.
3. Recovery
This is one of the most crucial factors while comparing MBR vs GPT. It determine how significantly each partition performs in terms of securing data in the disk.
On MBR, all partitions and boot data are stored in one place. So if in case, the data get overwritten or corrupted by any means, you will be going to run in trouble. Also, there is no way out that you may get to know about the data corruption until your system fails to boot or drive partitions gets vanished. However, it’s likely to get the recovery of the data, but that’s not certain for every time and case.
On the contrary, GPT is far more efficient and robust as it stores multiple copies of data across several disk partitions. Since it doesn’t rely on a single partition for the restoration of the data, you won’t be having any issues even if an unwanted event occurs. Additionally, GPT makes use of Cyclic Redundancy Check, which is an error detecting code that uses the CRC32 checksum, firmware, and bootloader to detect the issues on the partition map and data corruption. The mechanisms address the anomaly and run attempts to resolve it by either retrieving the data or repairing wherever possible.
This makes the GPT fundamentally more superior than MBR.
4. Compatibility
You should know the Boot Mode compatibility before deciding the ideal disk layout because this is something that determines the type of disk partitioning style your system supports. BIOS and UEFI are the two interfaces responsible for booting the Windows machine. If your system has a Legacy BIOS, it will only support Master Boot Record, whereas UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is compatible working with both MBR and GPT.
64-bit Windows 10, 8/8.1, 7, and Vista can be boot from a GPT drive if supports UEFI Boot interface. And similarly, 32-bit Windows 10 and 8/8.1 require a UEFI-based system to boot from a GPT drive except for Windows 7 and Vista. However, all the mentioned Windows version supports reading GPT drives and can use them for data.
MBR vs GPT – How and which one to Choose?
Choose GPT when:
- You have a Hard Disk larger than 2TB in size
- Your computer system supports UEFI Boot
Choose MBR when:
- You need compatibility for the old systems not supporting UEFI
Due to the number of limitations and lack of advantages, the MBR-based partitioning scheme has almost superseded by the GUID Partition Table.
Also Read: 5 Methods to Create Bootable Windows 10 USB or Disc
How to Check the Existing Partition Style of your Drive?
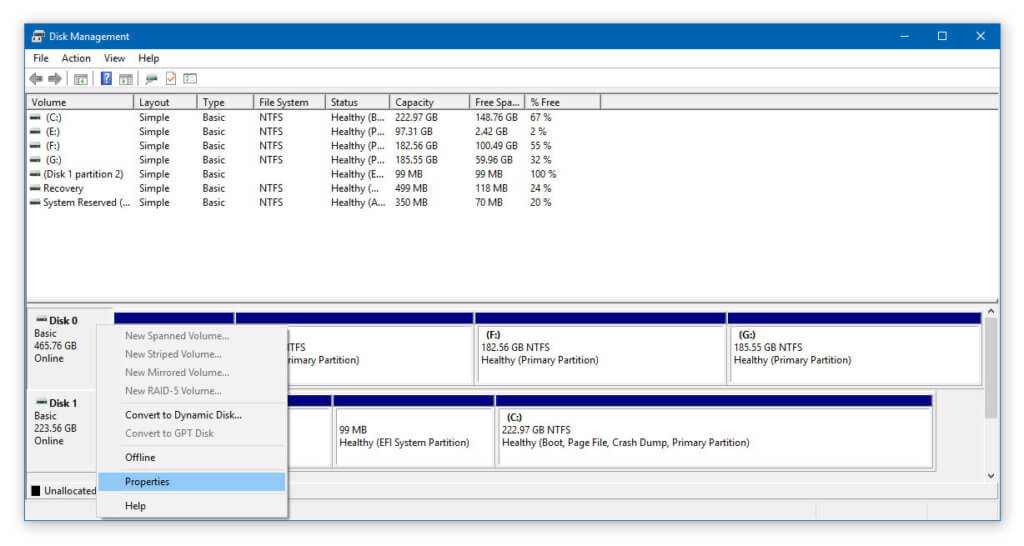
If you aren’t aware of the partition type your current system has allocated for, follow the steps given below:
- Press Windows key + X
- Select Disk Management and right-click on the Disk
- Tap on Properties >> Volume and under Disk Information you will have the Partition Style of your System.
Convert an MBR Disk into a GPT Disk
Now, for any reason, if you want to convert the existing MBR disk partition layout to GUID Partition Table, follow the method given below.
MBR2GPT
If you are a Windows 10 user, you already have this disk conversion tool on your system since it’s a part of the Window’s Creator Update. You can find MBR2GPT.EXE by navigating to the Windows\System32 directory. It converts a disk from the Master Boot Record (MBR) to the GUID Partition Table (GPT), and unlike traditional methods, it won’t modify or delete the system’s data on the disk.
First and foremost close all the programs accessing the disk. But before you start with the conversion, make sure that your computer system supports UEFI Boot Interface.
Step 1. Press Windows + X and click on Disk Management
Step 2. Locate the Disk you want to convert into GPT and note down its Disk Number.
Step 3. Next, search Command Prompt, right-click on it select “Run as administrator.”
Step 4. Validate the disk by entering the following command
Step 5. Once validated, enter the next command given below and hit enter
Step 6. After the system reboots, press the BIOS key (must be “Esc” or “Delete”) and under Firmware Settings menu change the Boot Mode to UEFI. Settings are often varied by the manufacturer, and even by machine models, so you have to look for the correct one to make changes.
Wrapping up
I hope you aren’t any longer skeptical about choosing the disk partitioning style between MBR and GPT. I’ve tried simplifying the tidbits around MBR vs GPT, but if still, you got any questions in your mind, type-in the comment box below.