You might have heard the term ‘HTTP Cookie’ or ‘Internet Cookie’ or simply Cookie. These are fairly common and essential in today’s Internet era. Maybe you recently started exploring more about the web or your curiosity has landed you here. In that case, we’ll tell you exactly what cookies are on a computer and what they do. Let’s dig in!
What are Cookies?

So, what are Internet Cookies? In simple English, a cookie is a small file put on your computer’s hard drive by a website you visited. These files contain small bits of data like your username, password, what options you choose on the site and what products you looked at.
A Cookie is created when a server connects and sends data to the user’s web browser. Let’s take an example where you visit a website and may be asked to fill your name, email and personal information. This information is then packaged into a file that is labelled with a unique ID to your computer.
Different types of Cookies?
There are two types of Cookies – Magic Cookies and HTTP Cookies. Both cookies fundamentally function the same way but have different use cases. A magic cookie is simply a packet of data that is exchanged between communicating programs. Typically, the data is not very meaningful to the recipient program and is only interpreted when the recipient passes it back to the sender or another program. This type of short packet is often used as an authentication token or password to a computer database or function.
While magic cookie is a broad term, HTTP cookies are specific to the web. The HTTP cookie is essential for web development and browsing. Without it, web pages won’t be capable of storing any browsing history.
HTTP Cookies
The HTTP Cookie term was coined after magic cookie for the modern Internet. Lou Montuilli, a computer programmer, had the idea of using magic cookies for web communications for the first time in 1994. He implemented the idea of virtual shopping cart technology for an e-commerce company that fixed their overloaded servers.
HTTP Cookie is a small packet of data that the server sends to your web browser. The browser may choose to store it and send it back to the server with the stored information. These can be used to store personal information, login details, personalization and tracking details. These HTTP Cookies act like your personal ID whenever you revisit the website.
Why is this important? Simple, it helps web servers identify you based on a “name-value” pair. Most of the times the browser asks your permission before it can store a cookie.
What are HTTP Cookies used for?
One of the most popular uses of HTTP Cookies is to store login information (known as authentication cookies). But they are also useful to remember user preferences, shopping carts, themes and more. Let’s take a look at some of the most common uses of Cookies and understand what are cookies used for on websites.
1. Personalization
Many websites offer customisable themes or settings like layout, language, location etc. HTTP Cookies enable websites to save all that information, so you don’t have to waste time setting preferences each time. This also enables websites to adapt content based upon each user and deliver personalised ads they might like.
2. Session management
A ‘session’ is simply the time spent by a user on the site and every activity performed during that time. By storing session information cookies help websites recall user login information, shopping carts and more so that the user doesn’t have to login or add items to the shopping cart every time they visit the website. This helps save your time and retrieve saved data in case of accidental shutdown of the page.
3. Web scraping
We’ve discussed how websites send cookies whenever you try to access them. Since web scraping unlike crawling involves making repeated requests to a server, it becomes crucial to have an HTTP cookies management protocol. When making a request, the right cookies need to be used to avoid being blocked.
If your request doesn’t contain the right cookies, there’s a good chance you’ll get an error, or in worst cases be identified as a suspicious bot and possibly get blocked. One of the solutions for this is to visit the main page first, collect cookies from there and use them for your web scraping requests.
4. Tracking
HTTP Cookies help websites in recording and analysing user’s interests and previous interactions. Shopping websites use these to show products based upon what you’ve viewed before. Similarly, news and sports sites will show you content according to what you might like to keep you hooked up.
First-Party vs. Third-Party Cookies
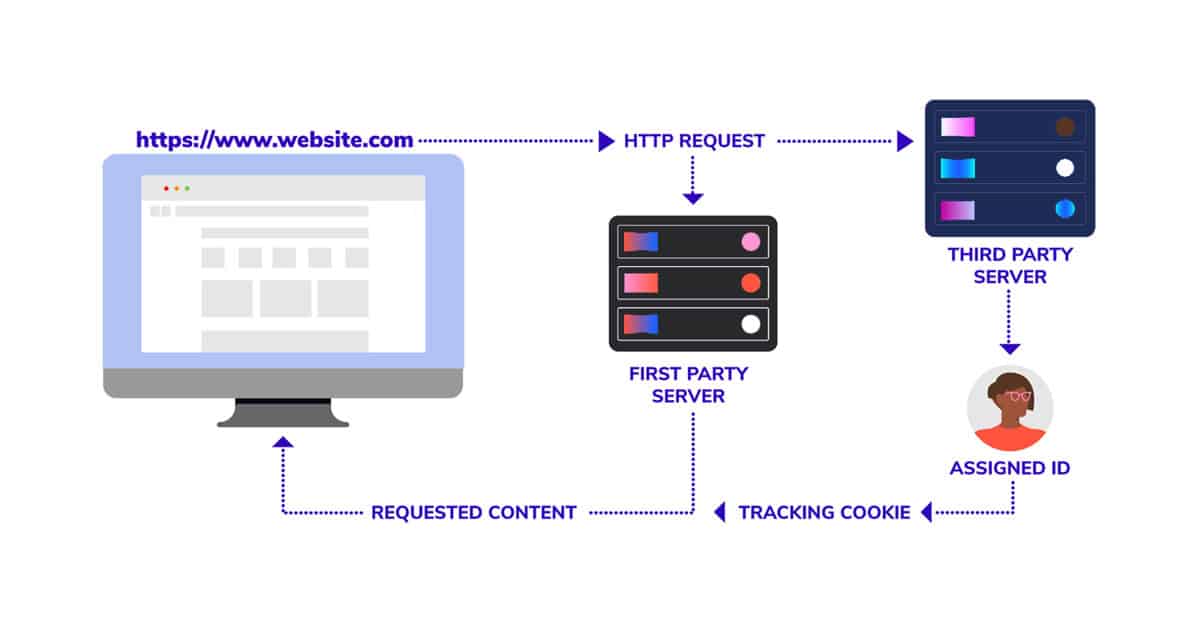
These are almost identical in their functioning and purpose but differ in terms of how they are created and used. There are advantages and disadvantages of using both, which we’ll find out in this section.
First-Party Cookies are created by the website directly when you visit. These are used to track user behaviour analytics data, game scores, language settings to provide a good user experience. These are usually safe as long as you’re visiting a trusted and reliable site. A good example would be when you visit a shopping site like Amazon, then the cookie directly interacting with Amazon will be a first-party cookie.
Third-Party Cookies are created by different websites than what you are currently viewing. These are accessible to any website that has access to the third-party’s server code. Third-party cookies are used for online advertising, retargeting and cross-site tracking. This is the reason why you start getting ads and emails for that dress you viewed but never purchased on Amazon. These are not always safe, and even Google has announced that it will phase out the third party cookies from Chrome by 2022.
Websites that use cookies almost always ask for your permission before they can send cookies, as failing to do so might attract legal attention. Cookies are completely optional, and you may choose to accept some or all of them, or none at all. So when should you allow or remove cookies?
Allowing cookies helps you get tailored experience with content that might be more relevant to you. For a website you trust or unless you’re really concerned about privacy, it’s usually fine to accept cookies. In most cases, cookies enhance web experience and save user’s time. On the flip-side, some companies won’t let you use their sites without allowing their cookies.
Removing cookies helps reduce legitimate risk of security and user privacy breach. It also resets website’s personalisation and tracking so you can enjoy a fresh experience. It’s a good idea to clear cookies from time-to-time unless you don’t want to lose any stored credentials. You’ll typically find the options for clearing and managing cookies in the Privacy (or sometimes History) section in your browser’s settings.
Conclusion
HTTP cookies are an integral part of the modern Internet. Their primary purpose is to identify users and adapt content based upon them. Cookies make it more convenient to use the web, but at the same time, can be troublesome if you don’t know what you are browsing or how to delete them.
Hopefully, this short guide has educated you on what internet cookies are and how to deal with them. The internet is growing at a revolutionary rate, which in turn makes data privacy a big topic of debate. Now that you know what the first step to protect your online privacy is, why not check what cookies are stored in your browser right now.