Human imaginations are always awesome. From the invention of the Computer in 1822 till 21st century, life is becoming easier, faster, and technological. Various inventions proved to be revolutionary. The rate at which technology is bouncing around rapidly, it becomes challenging to wrap your brain around it and all the abbreviations it follows.
Up until now, we have been closely associated with the terms VR (Virtual Reality) and AR (Augmented Reality). The concepts of VR and AR have been the subject line for most of the movies we have seen before and continue to see now. Different but connected. The only thing common between Virtual and Augmented Reality is that both alter our perception of the world; the difference, though, lies in how each of them does it.
Artificial hand for physically handicapped ones is a recent invention that works as per the commands of a person’s mind by codifying that person’s thoughts! How far we’ve come! It looks like a wonder. However, there is more to the world of realities than just AR and VR. Some realities extend beyond these two but haven’t known much. In this article, we will discuss all the realities including AR, VR, MR, DR, AV and HR in detail to understand the difference between them and how these realities alter our perception of the world.
What is Augmented Reality (AR)
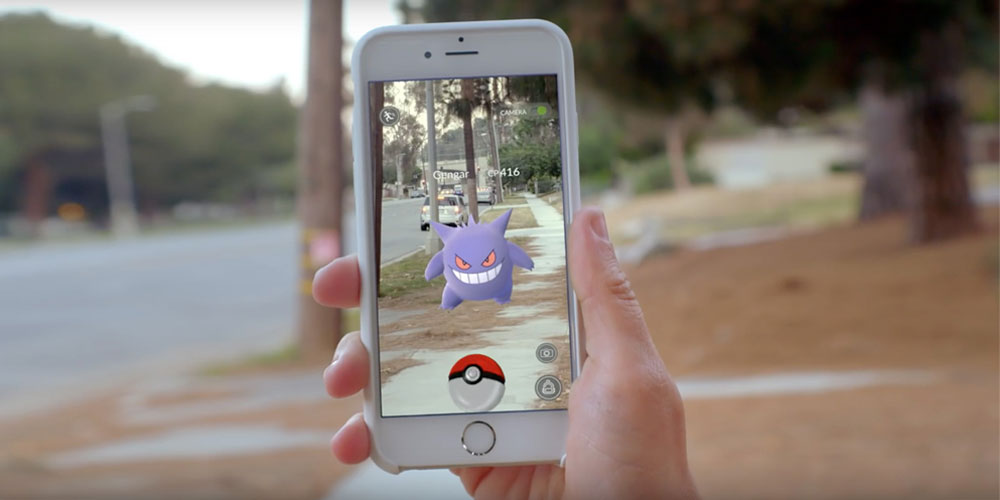

In augmented reality, the user sees an enhanced version of the physical world. This enhanced version of the physical world is made possible through digital visual, sound, and other stimuli elements brought together via technology. Nevertheless, the users are aware of being present in the real world irrespective of the other visual elements added using AR.
In simple words, AR gives us an enhanced version of the actual physical world that exists around us through the use of digital visual elements, sound, and other sensory stimuli, all delivered through the use of technology. AR is a 3D experience that combines both real-world and digital world objects and displays them in real-time. Pokemon GO and Jurassic World Alive are popular examples of augmented reality.
What is Virtual Reality (VR)
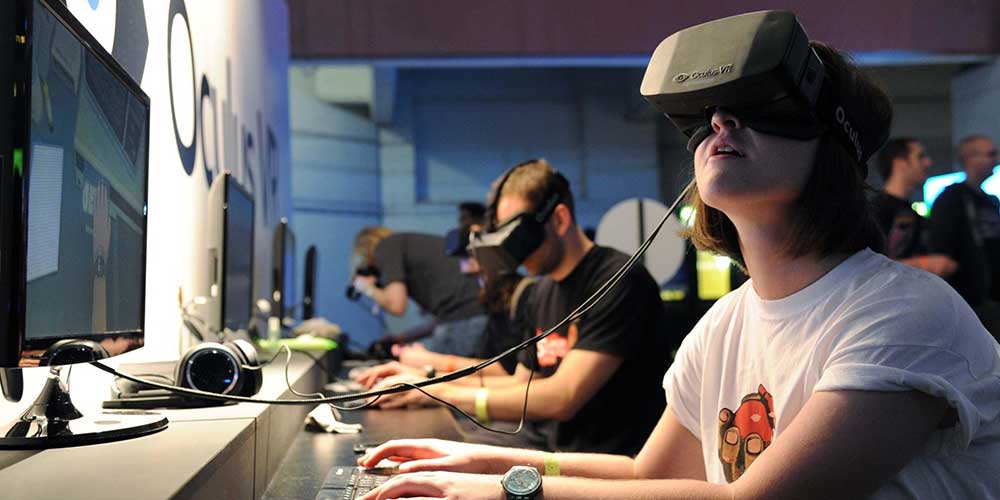

Total immersion is what makes a VR apps and games special – making the virtual reality experience so real that we forget the computer or the headgear and act exactly as we would in the real world.
The goal of the hardware is to create what appears to be a life-size, 3D virtual environment without the boundaries we observe in TV or computer screens. So whatever way we look, the screen mounted to our face follows us. Video is sent from the device to the headset, and the headsets, in return, might either use two feeds sent to one display or two LCDs, one per eye.
When we move our heads in any direction, the accelerometer in our phone and the GPS locate and project us into the virtual reality we see. And with headphones, we can hear sounds as if they are coming from different directions, giving us a completely immersive experience and making us feel like we’ve been transported somewhere else.
What is Mixed Reality (MR)
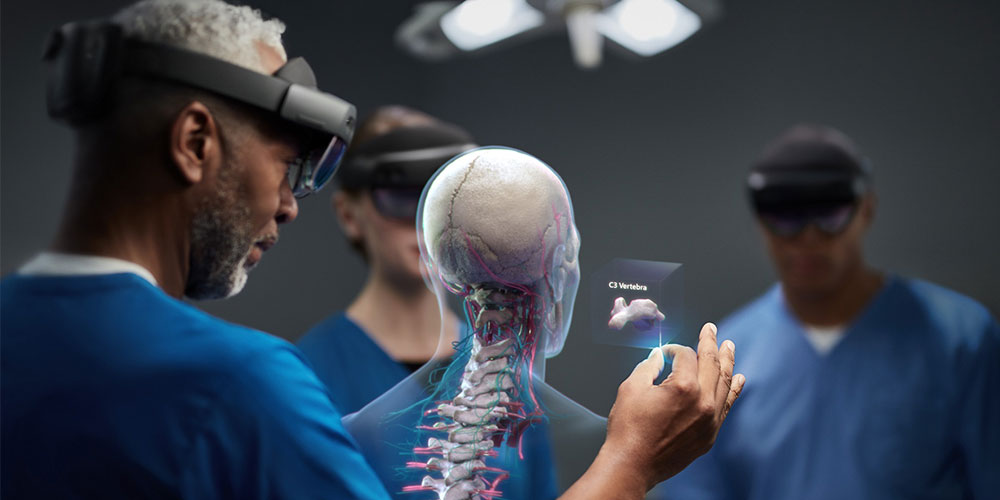

As the name suggests, Mixed Reality combines both VR and AR; wherein real-world objects interact with the digital ones. MR is one of the most recent innovations that revolves around extended technology, taking AR to another level.
With mixed reality, you can manipulate the digital images that are overlaid onto the real world. A great example of Mixed Reality is the Microsoft Hololens, wherein you wear a headset that is not precisely worn during VR. Instead, this headset allows you to see the real world, wherein you can place objects into this real world.
Unlike AR and VR, MR is where real and digital objects merge and interact together in real-time, allowing us to create new visualizations and an environment wherein physical and digital objects interact in real-time.
AR vs VR vs MR: What Separates the Three
| Augmented Reality | Virtual Reality | Mixed Reality | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perception | Overlays the digital world with real-world objects | A fully digital world utterly independent of the real world | Both real and virtual things are intertwined in Mixed Reality |
| User Presence | User Presence necessary for experiencing the imagery world | No user presence is required to experience the imagery world | User Presence necessary for sharing the imagery world |
| Boundaries | Partially Enclosed | Fully Enclosed | Not Constrained By Boundaries |
| Experience | A Real-world experience enhanced by digital detailing | Fully Synthetic Experience with No sense of the Real World | Manipulation of both real and digital world aspects |
| See-Through Capabilities | Partial See-through capability | No See-through Capability | Package of See-Through Capabilities |
What is Hyper Reality (HR)
Hyper-Reality is the ability of consciousness that allows us to differentiate between reality and a simulation of reality in advanced technological postmodern societies. Hyperreality is often referred to as something wherein real and fiction are often blended until a certain point where it becomes impossible to make a clear distinction as to where reality ends, and fiction begins and vice versa.
The concept of hyperreality has only been around ever since the technological advancements in media are impacting our day-to-day lives. Disneyland is a perfect example of hyperreality given its setting makes everything inside look realistic, taking a visitor’s imagination to a fantastic past.
What is Diminished Reality (DR)
Also referred to as deleted or delegation reality, Diminished Reality is a complement of AR. While AR adds more information and stimuli to the real world, DR focuses more on removing these elements of impulses from the real world.
Using a set of methodologies, DR conceals, eliminates, or completely deletes objects from a perceived environment in real-time, ultimately diminishing the entire reality created. In other words, DR is generally used to eliminate the gaps between real and virtual realities by erasing or removing objects.
DR is often used in helping the visually impaired by either lessening or erasing specific visuals. For example, a particular color in an image is modified using a computer application to make the visuals more suited for the visually impaired. DR is also used to fade down extraneous sounds or other sounds that interfere with a conversation that’s taking place in a noisy environment. Similarly, it is used to blur portions of a scene that aren’t too relevant.
What is Augmented Virtuality (AV)
Often Augmented Virtuality is mistaken to be the same as Mixed Reality. While there are a few similarities between the two, there is also a fair share of differences. Mixed Reality creates an environment wherein physical and digital objects interact in real-time. In contrast, Augmented Virtuality (AV) focuses on adding digital elements to a live view via a camera, smartphone, or other technical utility tools.
The user can manipulate Computer-generated imagery. For example, using a touchscreen, people can design their kitchen or bathroom by selecting and moving virtual appliances and fixtures around a digitally created room.
Conclusion
We hope our article was successfully able to walk you through the different forms of realities that exist. The rate at which technology is bouncing around rapidly, it becomes challenging to wrap your brain around it and all the abbreviations it follows.
While AR, VR, and MR are the three primary types of realties, they depend on AV, DR, and HR for many things.