Buying a new smartphone means thorough research of specs and in-depth comparison of devices in your desired range. But what if the smartphone company that owns your trust just lied about their spec sheet?
All phones have a chip that stores data in the long run, the chip stores apps, data, photos, music and the operating system as well. The chip can preserve data even when the phone is switched off, although the chip isn’t as fast as the RAM. The UFS 2.1 specifications are present in all the latest and recently launched phones, including the Samsung Galaxy S8.
The Samsung Galaxy S8 is one of the best smartphones I’ve ever come across. It has an incredible display wrap around the smallest bezel I’ve ever seen which Samsung is so proud to advertise anywhere they can think of. Also one of the specs they announced was the UFS 2.1. Though many people who already bought the Galaxy S8 don’t care about it, we care.
What is UFS 2.1?
Before I tell you what UFS 2.1 is, it is essential to know what UFS Stand for and what does it do. UFS stands for Universal flash storage. It is a flash storage specification for cameras, mobile phones and other consumer electronic devices.
The UFS brings a higher data transfer speed and increases the reliability to flash memory storage. It also reduces the confusion in the market and removes the need for having different adapters for different types of cards. The specifications have been supported by leading enterprises in the consumer electronics industry such as Nokia, Samsung, Sony Ericson etc.
The UFS 2.1 is the successor to the current eMMC standard for embedded NAND flash memory. UFS 2.1 technology offers improved security and higher performance in terms of data transfer speed on lower power consumption. It is an update on old version 2.0 which was published in 2013. So specifically, it has a huge improvement as compared to 2.0. UFS 2.0 chips are only capable of 500 MBPS read speed while UFS 2.1 can get any closer to around 750-800 MBPS.
How is UFS 2.1 Better Than UFS 2.0?
The UFS 2.1 has added new extensions to the UFS 2.0
- Support for multiple initiators for a UFS target device
- Support for CMD priority for UPIUs
- Support for FFU (Field Firmware Update) using Write buffer SCSI CMD
- Support for data count (update in UPIU field) in terms of block size
Does it matter?
Although the 250-800 MBPS leap looks huge, it won’t affect the overall OS performance. The only thing it will matter is with the sequential writing speeds. This will be more noticeable for people who always transfer a lot of files from any other devices.
Did Samsung Lie?
In the pictures below, you will find the difference in specifications of the Samsung Galaxy S8 when it was first released compared to the specifications that are currently being shown on Samsung’s website.
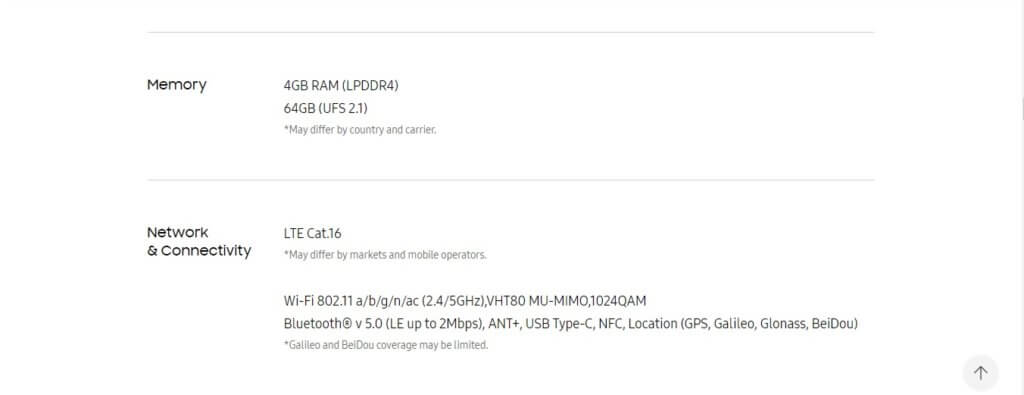
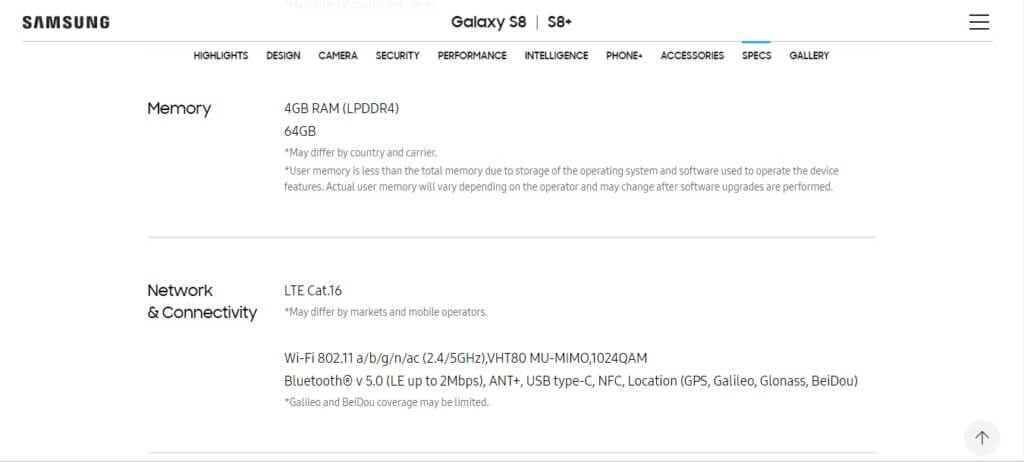
It still kind of annoying for the S8 users with Snapdragon 835 model to know that the advertised spec (which some expect) wasn’t really on their devices. Imagine being stuck on a 2013 technology while another model enjoys the 2016 update.
It is a sad time for Samsung. A really a sad time for the company we all love.
This is not the first time that a brand has misled its consumers by showing phone specifications that weren’t present. Huawei, in their P10 specification, showed a UFS 2.1 being used in their device while in reality an eMMC 5.1 was being used.
What do you think? Did Samsung lie, or is it just a horrible mistake? Tell us in the comment section below. While the UFS is fast, there are other ways to make your phone faster as well. You can do this overclocking your phone which would require your phone to be rooted. You can learn more about UFS and eMMC in the FAQs written below.
FAQs
UFS is a new format of expandable storage device that has been developed by Samsung. The UFS offers data transfer speeds that are five times faster than the UHS-I micro SD that used to be used.
The eMMC used to send data in one direction, which means it couldn’t read or write at the same time. The UFS can read and write at the same time, which means that it works at a speed much faster than eMMC. The eMMC can manage speeds of only up to 2GBPS while the UFS can handle the speed of 5.9GBPS in one lane.
The latest UFS specification that is currently being used is UFS 3.0. The UFS 3.0 spec doubles the per lane performance when compared to to the eUFS. It has also introduced a new 2.5 V VCC power supply that helps in consuming less power.
eMMC or Embedded Multimedia Card is a more affordable and is a lot slower than UFS
that is currently being used. eMMC’s are usually found in smartphones and other consumer electronic devices. The performance of the eMMC can be said to be somewhere between the speeds of an HDD and an SDD.
There are apps available on the play store that can find out whether your phone has UFS or eMMC. There are apps such as androbench that lets you know what kind of memory your phone uses